Wildfires are a significant threat to the environment and public health, with their reach extending beyond local communities and wildlife. Recent research has highlighted the interconnectedness between wildfires and meteorological systems, particularly mid-latitude cyclone activity, showcasing the broader implications of these natural disasters.
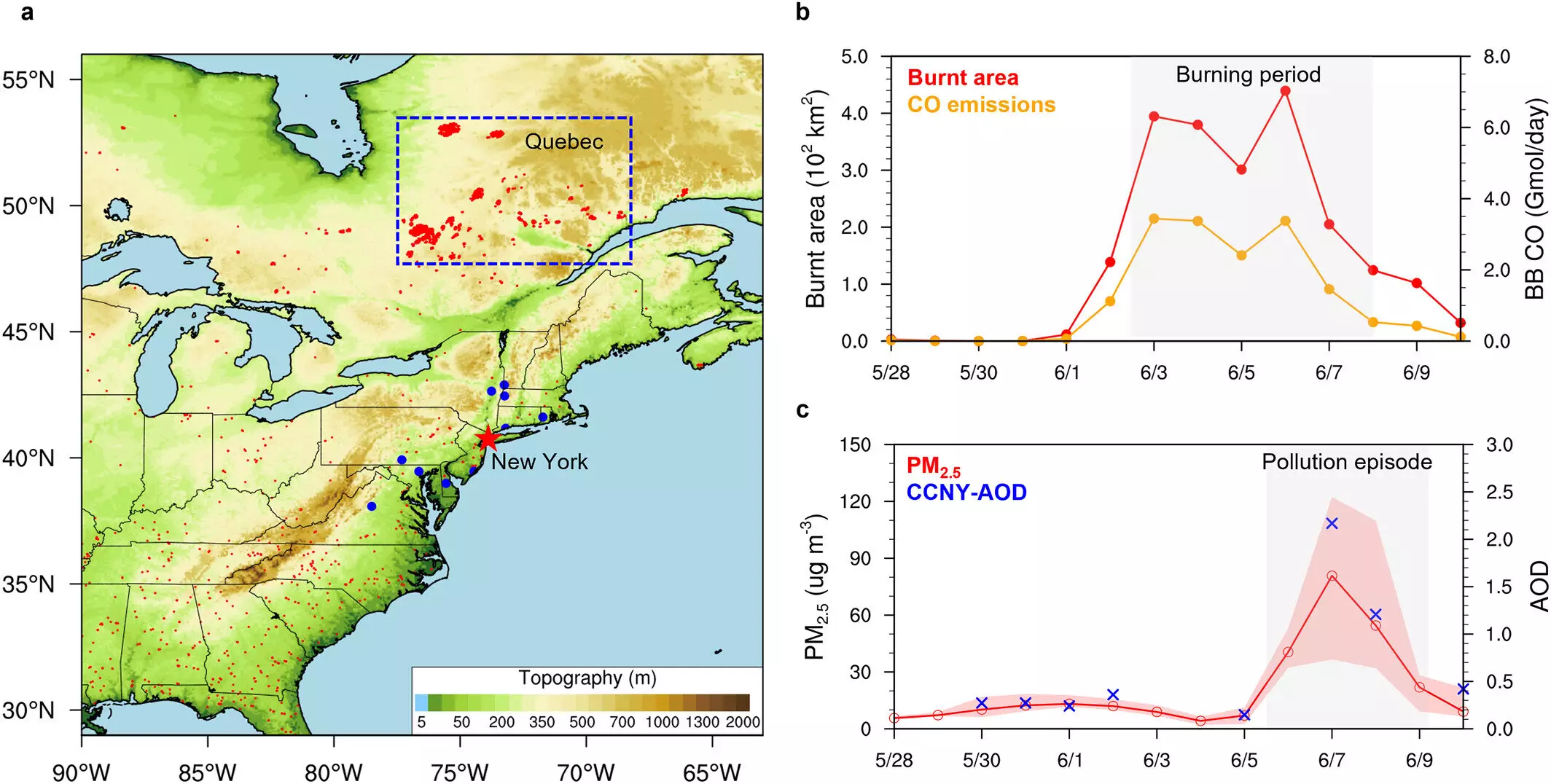
In June 2023, Quebec’s boreal forest experienced a devastating outbreak of wildfires, leading to widespread destruction and the release of a significant amount of CO2 into the atmosphere. The impact on air quality in eastern Canada and North America was severe, surpassing safe levels outlined by the World Health Organization. This case study serves as a stark reminder of the far-reaching effects of wildfires on both local and regional scales.
Research Findings
Dr. Zilin Wang and colleagues conducted a study utilizing high-resolution data on trace gas and particle emissions from biomass burning, combined with satellite observations of wildfire activity. Their research highlighted a strong correlation between cyclone activity and the transport of wildfire smoke across vast distances, impacting areas as far as New York. The stagnation of cyclones over affected regions deepened aerosol concentrations, exacerbating air quality issues and altering the energy balance in Earth’s atmosphere.
Impact on Meteorological Systems
The research revealed the complex interactions between wildfire smoke aerosols and meteorological processes, such as cloud formation and energy balance. Smoke aerosols were found to have varying effects on incoming solar radiation, either causing cooling or warming depending on their properties. Additionally, aerosols influenced surface wind speeds, atmospheric moisture, and air temperature, creating a positive feedback loop that intensified wildfire activity.
As the climate continues to warm, the prevalence of wildfires is expected to increase, emphasizing the importance of understanding the impact of smoke aerosols on meteorological systems. It is crucial to develop strategies to mitigate the effects of wildfires and prevent further exacerbation of extreme weather phenomena. This research serves as a stepping stone towards better preparedness and response to the interconnected challenges posed by wildfires and cyclone activity.
The study sheds light on the intricate relationship between wildfires and cyclones, underscoring the need for comprehensive research and proactive measures to address the environmental and public health risks associated with these natural disasters. By gaining a deeper understanding of these dynamics, we can work towards a more resilient and sustainable future in the face of escalating climate change impacts.

Leave a Reply