Recent advancements in material science have led to the exploration of van der Waals magnets, a class of materials that exhibit unique electronic and magnetic properties. A critical component of this research involves understanding excitons—quasi-particles composed of electrons and their corresponding “holes” that act as positive carriers within a crystal lattice. The research team at Brookhaven National Laboratory has made significant progress in revealing the dynamics and formation of excitons in nickel phosphorus trisulfide (NiPS3), a prominent example of van der Waals magnets. As technology evolves, the findings of this study could catalyze innovative developments in areas such as information technology and data storage.
NiPS3 has emerged as a focal point for researchers interested in the interplay of electronic and magnetic properties. Its unique structure provides a fertile ground for studying excitons in a context where magnetism significantly affects their behavior. This characteristic makes NiPS3 particularly interesting: it not only holds promise for advancing our understanding of quantum materials, but it could also pave the way for revolutionary technologies that harness these properties for practical applications, particularly in fields that demand enhanced efficiency in information storage and processing.
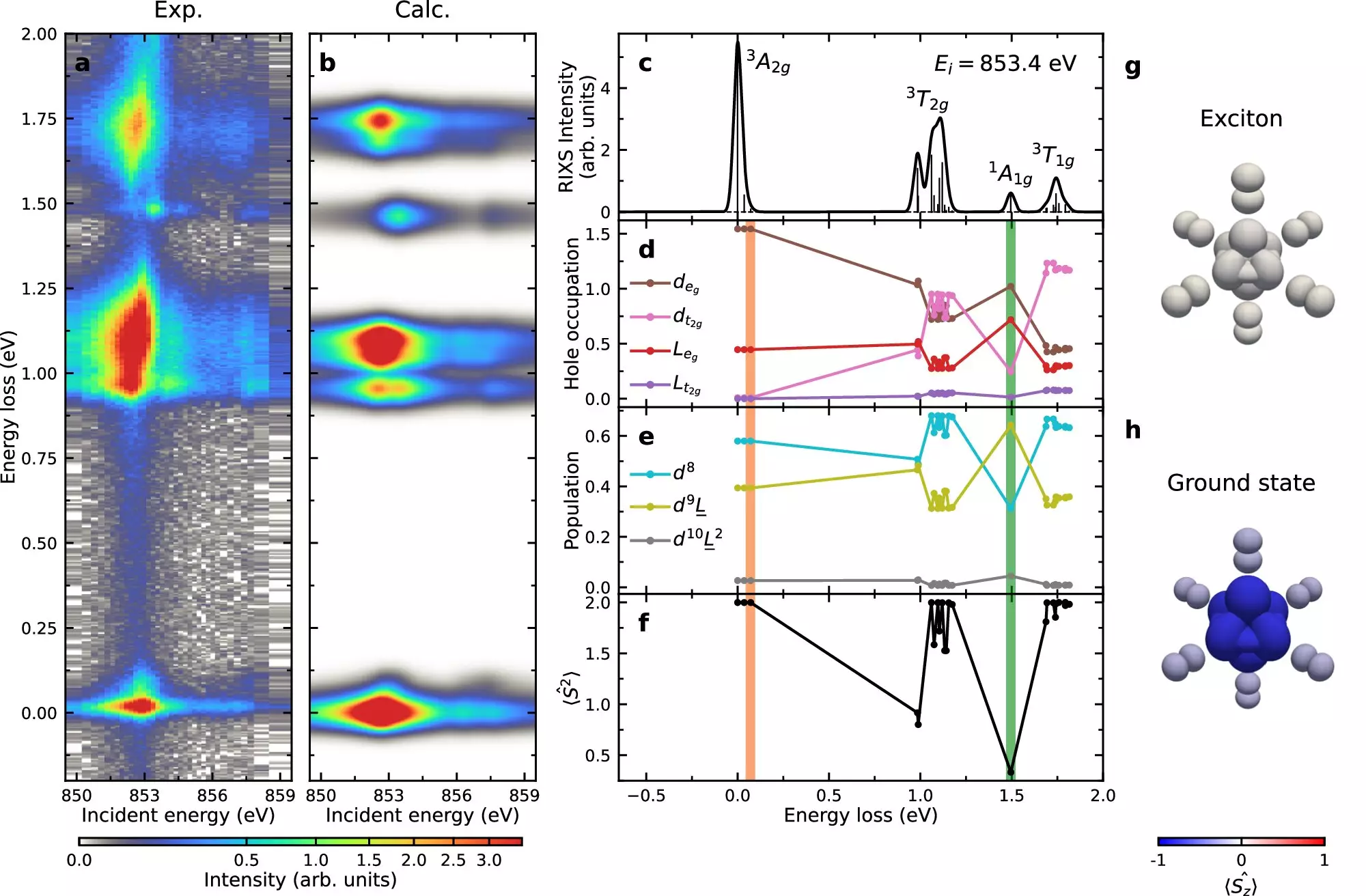
In their study, the researchers employed resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) to investigate the excitonic phenomena present in NiPS3. This sophisticated technique involves using intense beams of X-ray light to probe the electronic structure of the material and capture the interactions that take place within it. By examining how X-ray photons scatter off electrons, the researchers at Brookhaven were able to collect detailed information regarding the excitons’ formation, behavior, and motion within the crystal. The use of RIXS has empowered scientists to glean insights that were previously obscured, enabling a deeper understanding of the fundamental interactions at play.
One of the principal findings of the Brookhaven study was the identification of the Hund’s exchange interaction as a key factor in the formation and propagation of excitons in NiPS3. This principle plays a vital role in determining the energy associated with various spin configurations of electrons within the material. By applying this understanding, the researchers were able to demonstrate how excitons navigate the crystal structure and how their movement mirrors the dynamics of other excitations such as double-magnons. This correlation underscores the interconnectedness of electronic and magnetic properties in van der Waals magnets, emphasizing the complex nature of material behavior.
As research progresses, the tools and techniques available for studying excitons and related phenomena will continue to evolve. Future advancements in RIXS and other imaging modalities, such as electron microscopy, hold the promise of illuminating even more intricate aspects of excitons and their interactions with magnetic fields. The potential applications of understanding excitons and their relationship with magnetism are substantial, suggesting pathways toward developing next-generation technologies in data processing, storage systems, and quantum computing. Such breakthroughs could lead to devices that are not only faster but also more efficient than their conventional counterparts.
The exploration of excitons within materials like NiPS3 is an exemplary case of how foundational research in physics can intersect with technological innovation. The findings reported by the Brookhaven research team mark a significant step toward unraveling the complex interplay between electronic and magnetic behaviors in van der Waals magnets. As the scientific community continues to investigate these phenomena, the implications for future technologies could be far-reaching, catalyzing a new era of advancements deeply rooted in the principles of quantum mechanics and material science. The quest to understand and manipulate excitons within these intriguing materials holds a promise that extends beyond theoretical exploration into tangible benefits for future generations.

Leave a Reply