In today’s eco-conscious world, electric vehicles (EVs) represent a pivotal shift in transportation. As the primary alternative to fossil fuel-powered cars, their success hinges significantly on the efficiency and sustainability of battery technology. Lithium-ion batteries, the backbone of this revolution, have traditionally relied on expensive and environmentally questionable materials like nickel and cobalt. However, emerging research points toward lithium manganese oxide (LiMnO2) as a transformative solution. By leveraging the wealth of manganese, scientists are not only optimizing energy output but also addressing the pressing need for sustainability in the automotive sector.
Breaking the Mold: The Promise of LiMnO2
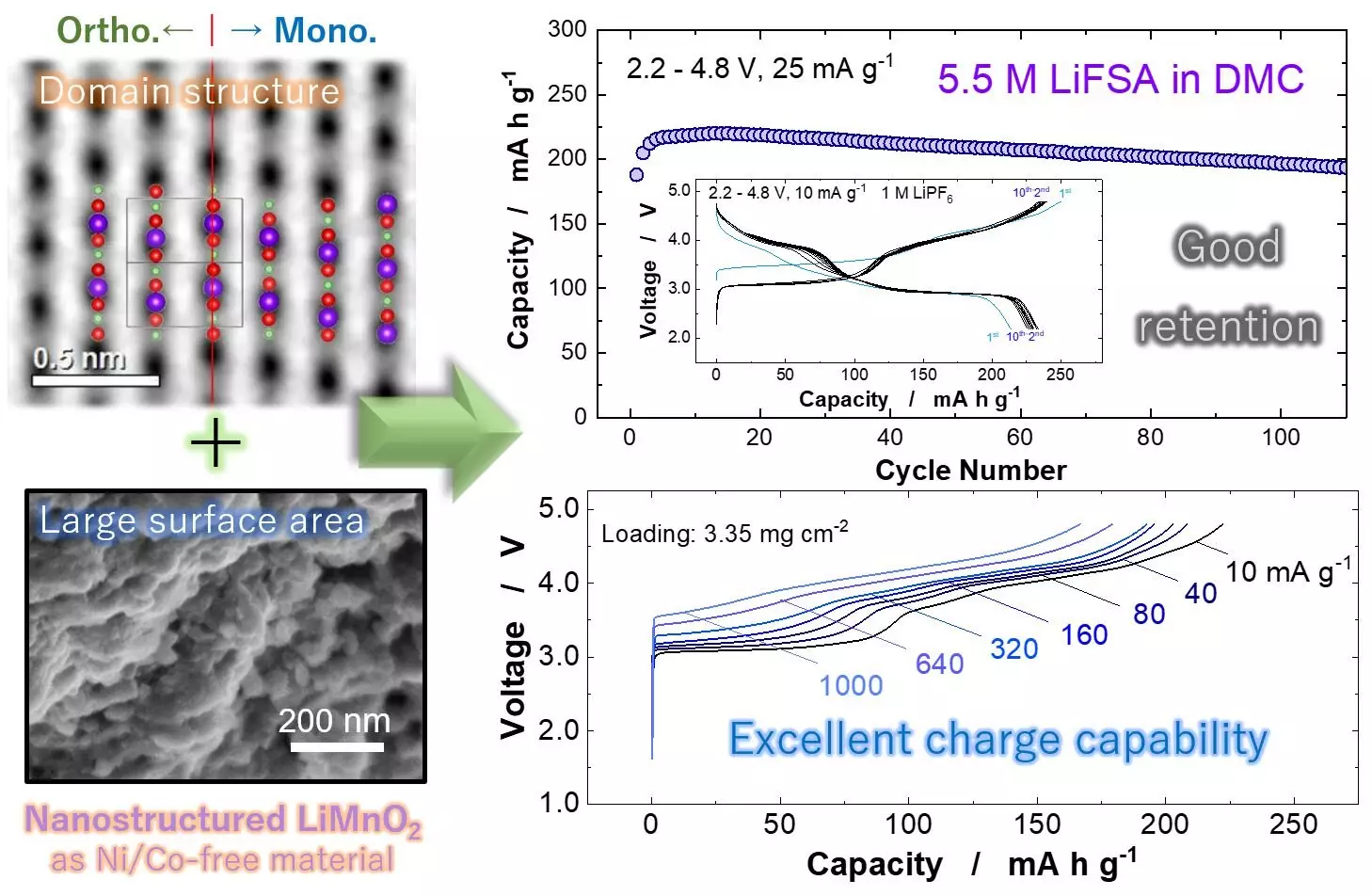
Lithium manganese oxide has long been overlooked due to its past performance limitations, but recent studies reveal its potential as a robust alternative to conventional materials. The key lies in the monoclinic layered structures of LiMnO2, which allow for superior structural phase transitions. Through groundbreaking research conducted by a team led by Naoaki Yabuuchi, nanostructured LiMnO2 has been developed that significantly enhances storage capacity and charging speeds. This innovation could mean the difference between a viable green future and the continued reliance on unsustainable fossil fuels.
Performance Metrics: A Game Changer for Energy Density
One of the primary metrics when evaluating battery materials is energy density—the amount of energy stored per kilogram. Recent findings reveal that nanostructured LiMnO2 can achieve an impressive 820 watt-hours per kilogram (Wh kg-1). This surpasses the energy density of traditional nickel-based batteries, which hover around 750 Wh kg-1, and places LiMnO2 in a competitive position against even the most cutting-edge lithium-based alternatives. The ability of LiMnO2 to maintain this energy density without the common issue of voltage decay—where performance diminishes over time—highlights its potential in the fast-evolving landscape of EV technology.
Technological Breakthroughs: Navigating Challenges
Despite the impressive capabilities of nanostructured LiMnO2, researchers must address challenges associated with manganese dissolution. This phenomenon can lead to performance degradation over time due to environmental interactions. However, recent advancements propose solutions to mitigate this risk through concentrated electrolyte solutions combined with a lithium phosphate coating. This synergy not only helps preserve the integrity of the manganese ions but also ensures extended lifespan for battery applications, marking a significant step forward in battery technology.
The Road Ahead: Commercial Viability and Sustainable Practices
As we look to the future, the implications of this research extend well beyond laboratory successes. The potential for nanostructured LiMnO2 to become commercially viable is substantial, particularly in the luxury electric vehicle market where performance meets sustainability. The demand for ethically sourced materials paired with efficient energy storage will likely drive manufacturers to adapt to these innovations.
Furthermore, the move toward LiMnO2 is not merely a scientific trend; it reflects a larger shift in the automotive industry towards responsible production practices. Emphasizing the importance of sustainability is not just beneficial for business but essential for the planet. By transitioning to more sustainable battery solutions, we can minimize the ecological footprint created during the extraction and processing of traditional materials like nickel and cobalt.
Final Thoughts on the Future of Battery Technology
It’s clear that research into nanostructured LiMnO2 is reshaping the landscape of rechargeable battery technology. The blend of high performance, cost-effectiveness, and low environmental impact makes this innovation a beacon of hope in our quest for a sustainable future. As electric vehicles continue to gain traction, investing in such transformative technologies will be crucial. The road ahead is not without challenges, but the commitment to innovative solutions like LiMnO2 may very well pave the way toward a cleaner, greener tomorrow in transportation.

Leave a Reply