Recent advancements in water quality monitoring technology have emerged from a remarkable study conducted by researchers at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science under the Chinese Academy of Sciences. These scientists have developed cutting-edge microfluidic sensor arrays that can detect and visually represent heavy metal contamination in real time. This breakthrough offers a robust solution not just for scientists but for everyday users concerned about water safety, addressing one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time.
Understanding the Threat of Heavy Metals
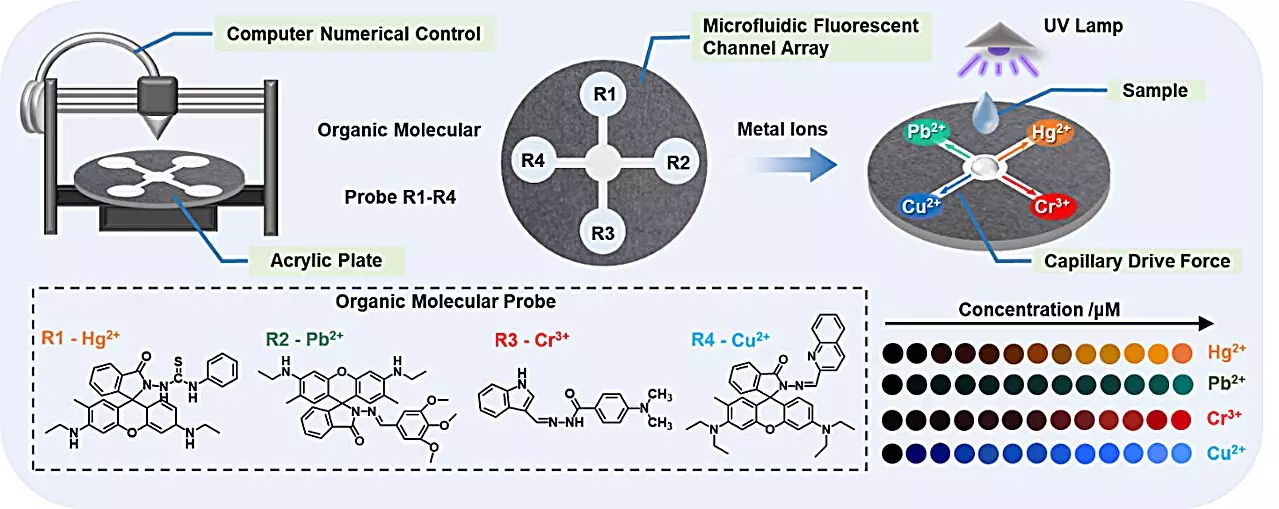
Heavy metals like mercury, lead, chromium, and copper are pervasive pollutants that infiltrate our water supplies, posing a significant risk to ecosystems and public health. Their detection has traditionally been challenging, primarily due to the slow processes involved in analytical methods that isolate each metal for testing. This inefficiency can delay responses to contamination, allowing harmful materials to linger in our water systems. The research team led by Prof. Jiang Changlong recognized the need for a more effective approach to tackle this critical issue.
Microfluidic Technology: A Game Changer
The team’s innovative response entailed the integration of microfluidic technologies with sensitive fluorescent probes, showcasing an elegant interplay between scientific ingenuity and practical application. By designing arrays on acrylic substrates using capillary forces, they created complex microfluidic channels capable of conducting multiple tests simultaneously. This experimental setup dramatically enhances detection speed and efficiency, allowing for rapid assessments of water quality that were previously unattainable.
The array utilizes organic fluorescent probes that bind selectively to specific heavy metal ions, causing them to emit distinctive fluorescence signals. This not only makes detection of these metals intuitive but also provides an easily interpretable visual cue for users. Such advancements democratize the power of scientific monitoring, making it accessible even to those without technical expertise.
A User-Friendly Monitoring System
What sets this microfluidic sensor apart is its seamless integration with widely available technology. When paired with a smartphone utilizing color recognition software, users can not only detect heavy metals but also quantify their concentrations instantaneously. This feature transforms the experience of water quality monitoring into a hassle-free process, empowering individuals to track their water safety proactively. Imagine being able to check the quality of tap water with just the tap of a phone screen—this innovation makes it possible.
Real-World Implications of This Technology
The implications of these developments are significant. As urbanization continues to expand and industrial activities increase, the necessity for effective water testing becomes even more critical. The ability to monitor heavy metal levels in real time opens opportunities for immediate responses to pollution, safeguarding both environmental health and human safety. Communities can leverage such technology to ensure their water remains safe, echoing a societal shift toward greater accountability in environmental management.
By essentially flipping the script on water quality testing, this research holds the promise not just of better technology but of an empowered public that can take actionable steps toward safeguarding their own health. As researchers like Prof. Jiang Changlong continue to innovate, we can look forward to a future where clean, safe drinking water is no longer a luxury but a standard.

Leave a Reply